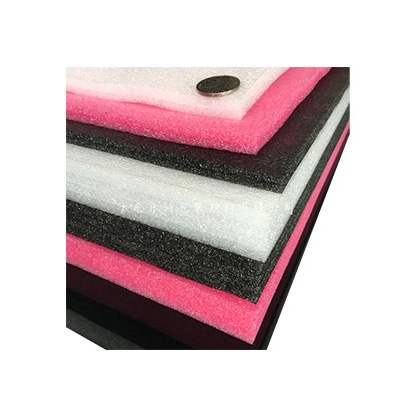
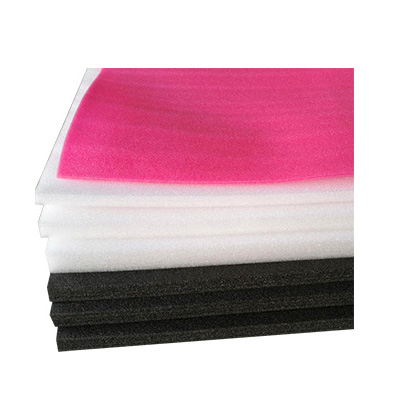
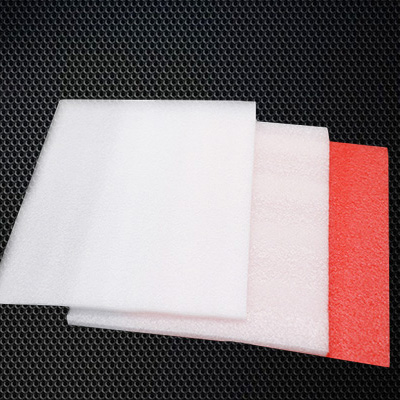
EPE Foam Board
EPE foam board is a type of closed-cell foam material made from polyethylene (PE) through a physical foaming process. Known for its lightweight, flexibility, shock resistance, and water resistance, it is widely used in packaging, construction, industry, and other fields. Below is a detailed breakdown:
-
Raw Materials:
Primarily composed of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) resin, mixed with blowing agents (e.g., butane), anti-aging agents, flame retardants, etc. The raw materials form a honeycomb structure of independent air bubbles through high-temperature melting, extrusion, and foaming.
-
Production Process:
Raw materials are heated and melted in an extruder, mixed with blowing agents, and extruded through a mold into a continuous sheet. After cooling and cutting, the final board is formed. Unlike EPE foam rolls, EPE foam boards are directly cut into blocks or sheets instead of being wound into rolls.
-
Shock Absorption & Cushioning:
The independent bubble structure absorbs impact forces, protecting items from collision damage—superior to traditional EPS foam boards in this regard.
-
Waterproof & Moisture-Resistant:
The closed-cell structure blocks water penetration, making it suitable for humid environments (e.g., cold chain packaging, building insulation).
-
Eco-Friendly & Recyclable:
Free of harmful substances like formaldehyde and benzene, it is recyclable and emits no irritating gases when burned, meeting environmental standards.
-
Lightweight & Easy to Process:
Low density (10–30kg/m³), it can be cut, punched, or laminated with non-woven fabric or aluminum film to meet customized needs.
-
Thermal Insulation:
The bubble structure reduces heat transfer, providing moderate thermal insulation for applications like building walls and greenhouses.
-
Packaging:
-
Precision Instruments: Inner packaging for electronics, glassware, and ceramics to provide shock protection.
-
Cold Chain Transportation: Used as thermal insulation to extend the shelf life of fresh food.
-
Construction & Home Use:
-
Thermal & Sound Insulation: Applied in wall and roof insulation or as floor soundproofing mats.
-
Home Decor: Used to make sofa cushions, yoga mats, and baby crawling mats for their softness and anti-slip properties.
-
Industrial & Automotive:
-
Equipment Protection: Cushioning liners for large machinery and pipelines to prevent transport wear.
-
Automotive Interiors: Filling for seats and soundproofing layers in car doors to enhance comfort.
-
Sports & Medical:
-
Protective Gear: Cushioning layers in helmets and knee pads to reduce sports impacts.
-
Medical Packaging: Sterile packaging for medical devices, offering water resistance and safety.
-
Dimensions:
-
Thickness: Common sizes range from 0.5–10 cm (e.g., 2cm, 5cm, 10cm), with custom thicknesses available.
-
Length & Width: Standard size is 1m × 2m, but it can be cut into any shape as needed.
-
Surface Treatment:
-
Laminated Layers: Single or double-sided lamination with aluminum film, non-woven fabric, or aluminized film to enhance reflectivity, anti-static properties, or abrasion resistance.
-
Color: Predominantly white, but can be colored with masterbatches to create black or multicolor boards.
|
Material
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
Applications
|
|
EPE Foam Board
|
Flexible, shock-resistant, eco-friendly, easy to process
|
Slightly lower thermal insulation than EPS foam board
|
Precision packaging, home decor, sports protection
|
|
EPS Foam Board
|
High strength, excellent thermal insulation, low cost
|
Brittle, non-recyclable, poor environmental performance
|
Building insulation, disposable packaging
|
|
Plywood
|
High strength, stable structure
|
Heavy, non-shock-resistant, non-recyclable
|
Furniture framing, construction formwork
|
|
Sponge
|
Soft, breathable
|
Poor water resistance, prone to mold
|
Sofa filling, filtration materials
|
-
Parameter Selection:
-
Density: Higher density (e.g., 30kg/m³) offers stronger compression resistance, ideal for heavy equipment packaging.
-
Thickness: Choose based on protection needs—10cm for building insulation, 2cm for general packaging.
-
Environmental Certifications:
Prioritize products with ISO 14001 certification to ensure environmentally friendly production processes.
-
Cost Consideration:
EPE foam boards are slightly more expensive than EPS foam boards but offer superior comprehensive performance (durability, recyclability).
EPE foam board, a sheet-form variant of EPE foam, is an ideal choice for packaging, construction, and industrial applications due to its cushioning, waterproof, and eco-friendly properties. Compared to EPE foam rolls, its thicker structure and stable form make it excel in scenarios requiring support or a flat surface. With rising environmental requirements, EPE foam board is expected to further replace traditional foam materials, driving the development of green packaging and building materials.









 Contact WeChat
Contact WeChat